In a significant breakthrough, researchers at RMIT University in Australia have found a way to replace the flammable electrolyte in lithium iron batteries with cheaper and less flammable water. This innovation could remove the fire risk from devices entirely, making them much safer for use in various applications.
Game-Changer for the Electric Vehicle Industry
The new water-based batteries could be a game-changer for the electric vehicle (EV) industry, where lithium batteries have long dominated the market. However, lithium batteries can catch fire due to thermal runaway, a chemical reaction that creates even more heat and can cause serious issues.
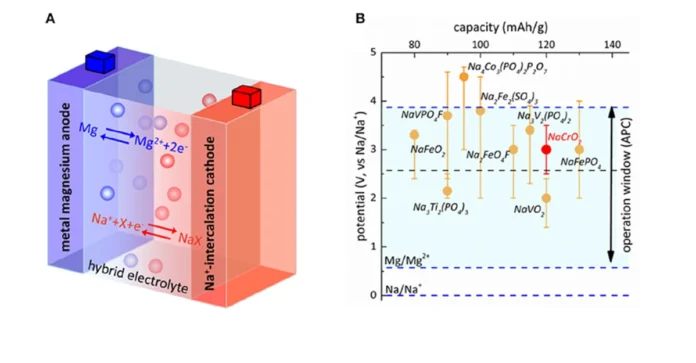
Researchers say that magnesium-based water batteries could replace lithium-ion batteries in EVs in the next 1-3 years, giving lithium-ion a real rival between 5-10 years from now. These batteries have the potential to be much cheaper than lithium batteries and could solve several issues that lithium batteries have, including being affected by heat.
The RMIT team isn’t the only Australian group looking at water batteries. In January, University of New South Wales researchers made a breakthrough with aqueous rechargeable zinc battery technology, solving dendrite problems. Dendrites are spiky crystal growths on the anode of the battery that can cause batteries to short circuit and reduce their overall lifespan.
The zinc anode dendrites can cause batteries to short circuit, but the team has cured this problem by coding affected battery parts with a metal called bismuth and its oxide, known as rust, as a protective layer to prevent dendrite formation. This innovation has made the batteries last significantly longer, making them ideal for high-speed and intensive use in real-world applications.
The new water batteries have already achieved an energy density of 75 W hours per kilogram, which is only about 30% of the energy density of batteries in a Tesla vehicle. However, this energy density is sufficient for many applications, such as 12-volt batteries in cars.
The new water batteries could also solve the problem of taking electric scooters, bicycles, or skateboards on airplanes. Currently, lithium-ion batteries are a significant issue for airplanes due to the risk of fire. However, water-based batteries are not flammable and could be a perfect solution for such situations.
The new magnesium-based water batteries could be a game-changer for the EV industry and could replace lead-acid batteries in the next few years. These batteries have the potential to be much cheaper than lithium batteries and could solve several issues that lithium batteries have, including being affected by heat and being a fire risk. The new water batteries could also solve the problem of taking electric scooters, bicycles, or skateboards on airplanes.
How do magnesium-based water batteries work?
Magnesium-based water batteries work by replacing the electrolyte in lithium-ion batteries with water, making them less flammable and potentially cheaper. These batteries use magnesium and zinc, which are abundant, inexpensive, and less toxic than other alternatives, reducing manufacturing costs and environmental risks. The batteries have an energy density of 75 W hours per kilogram, which is about 30% of the energy density of Tesla vehicle batteries. The researchers believe that these batteries could replace lead-acid batteries in the next few years and give lithium-ion a real rival in the next 5 to 10 years.
The future of batteries: magnesium-based water batteries?
The future of batteries is evolving with the emergence of magnesium-based water batteries, poised to revolutionize energy storage. Researchers at RMIT University in Australia have made significant advancements by replacing the electrolyte in lithium-ion batteries with water, eliminating fire risks associated with traditional batteries. These innovative water batteries, utilizing materials like magnesium and zinc, offer a safer and more cost-effective alternative to lithium-ion batteries. With an energy density of 75 W hours per kilogram, these batteries are positioned to replace lithium-ion batteries within the next 1 to 3 years and potentially challenge lithium-ion batteries within 5 to 10 years. The use of water as an electrolyte not only enhances safety but also reduces manufacturing costs and environmental impact. Additionally, Australian researchers are not alone in this endeavor, as other institutions are also exploring water-based battery technologies to address challenges like dendrite formation and enhance battery lifespan. The integration of water batteries with solar panels showcases efficient renewable energy storage solutions that are both effective and cost-efficient. The future applications of magnesium-based water batteries span across various industries, from mobile phones and cars to grid-scale energy storage, offering a promising solution to current battery limitations.
What are the challenges in developing magnesium-based water batteries?
Developing magnesium-based water batteries presents several challenges that researchers are actively addressing. One significant challenge is the formation of dendrites, which are spiky crystal growths that can occur on the anode of the battery, leading to short circuits and reduced battery lifespan. To combat this issue, researchers have coated affected battery parts with a protective layer made of bismuth and its oxide to prevent dendrite formation. This innovation has significantly improved the performance and lifespan of water batteries, making them comparable to commercial lithium-ion batteries in the market. Another challenge in developing magnesium-based water batteries lies in increasing their energy density. Researchers are exploring the use of new nanomaterials as electrode materials to enhance the energy density of these batteries further. By improving the energy density, water batteries can become more efficient and suitable for high-speed and intensive real-world applications. Additionally, while water batteries offer a safer and potentially more cost-effective alternative to traditional lithium-ion batteries, there are still considerations regarding their widespread adoption. Researchers believe that magnesium-based water batteries could replace lead-acid batteries and lithium-ion batteries within the next 1 to 3 years and potentially rival lithium-ion batteries within 5 to 10 years. The versatility of these batteries spans across various applications, from mobile phones and cars to grid-scale energy storage, indicating a promising future for this emerging technology.
How do magnesium-based water batteries compare to other types of batteries?
Magnesium-based water batteries offer a promising alternative to other types of batteries due to their safety, cost-effectiveness, and environmental benefits. These batteries replace the flammable electrolyte in lithium-ion batteries with water, reducing the risk of fire incidents significantly. They use magnesium and zinc, which are abundant, inexpensive, and less toxic than other materials used in batteries. The energy density of these batteries is 75 W hours per kilogram, which is about 30% of the energy density of Tesla vehicle batteries. Researchers at RMIT University in Australia have successfully developed these batteries, aiming to replace lead-acid batteries within the next few years and potentially rival lithium-ion batteries in the next 5 to 10 years. The use of water as an electrolyte makes these batteries safer and more commercially viable, addressing concerns related to fire risks associated with traditional lithium-ion batteries. Additionally, the manufacturing costs are reduced as water is cheaper than lithium, and the electrolyte formulas used are cost-effective. The team behind these magnesium-based water batteries has also focused on sustainability by designing them for safe disposal and recycling, contributing to a more environmentally friendly approach to energy storage technology
What are the potential environmental benefits of magnesium-based water batteries?
The potential environmental benefits of magnesium-based water batteries are significant and multifaceted. These innovative batteries offer a safer and more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries. By utilizing materials like magnesium and zinc, which are abundant, inexpensive, and less toxic than other alternatives, water batteries contribute to reducing manufacturing costs and minimizing environmental risks associated with battery production. One key environmental advantage of magnesium-based water batteries is their reduced fire risk. By replacing the flammable electrolytes found in traditional batteries with non-flammable water, these batteries eliminate the potential for fires in devices, making them a safer option for various applications. This enhanced safety feature not only protects users but also reduces the risk of environmental damage caused by battery-related fires. Moreover, the use of water as an electrolyte in these batteries offers a cost-effective solution compared to lithium-ion batteries. Water is a readily available and inexpensive resource, making the overall production of magnesium-based water batteries potentially more affordable. Additionally, the electrolyte formulas used in these batteries are not as costly as those in lithium-ion batteries, further contributing to their economic viability. Furthermore, the recyclability and reusability of materials in magnesium-based water batteries present an environmentally friendly end-of-life disposal solution. These batteries can be safely disassembled, and their components can be reused or recycled, addressing the disposal challenges faced by consumers, industries, and governments globally with current energy storage technologies. Overall, magnesium-based water batteries represent a promising advancement in battery technology that not only offers improved safety and cost-effectiveness but also demonstrates a commitment to environmental sustainability through reduced fire risks, lower manufacturing costs, and recyclability of materials.



